-
-
-
About TMTS
-
Exhibitor
-
Visitor
-
Press
-
Travel
-
- About TMTS
- Exhibitor
- Visitor
- Press
- Travel
2026-01-02
Global Manufacturing and Machine Tool Industry Outlook: 2025-2026
In 2025, the global manufacturing sector is experiencing a phase of moderate recovery accompanied by increasing structural divergence. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the OECD, global economic growth is expected to remain around 3%. Amid persistent inflation, elevated interest rates, and geopolitical uncertainties, overall manufacturing recovery remains restrained. However, investment driven by high value-added industries such as AI, semiconductors, and aerospace continues to expand, serving as the primary engine of growth.
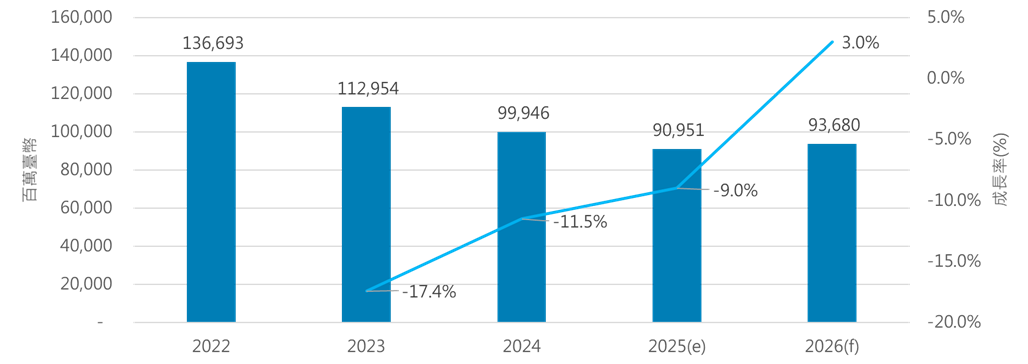
Source: IEK Consulting, ITRI
Following a downturn in 2024, the global machine tool industry is expected to gradually recover through 2025 and 2026, with growth concentrated in high-end applications. Key drivers include aerospace machining of titanium and aluminum alloys, semiconductor and precision component manufacturing, and the replacement of smart manufacturing equipment. Smart machine tools integrating automation, sensors, edge computing, and AI-based predictive maintenance have become a common pathway for manufacturing upgrades worldwide, boosting demand for core components such as controllers, spindles, linear guides, and ball screws.
Regional Market Dynamics and Supply Chain Shifts
Regional demand remains highly differentiated. Economic slowdown in China has dampened investment, while the United States and Europe face inflationary pressure, high energy costs, and cautious capital spending. In contrast, India and Southeast Asia have emerged as major growth markets, supported by manufacturing expansion and global supply chain restructuring.
Taiwan’s manufacturing sector continues to grow on the back of AI servers, semiconductor expansion, and electronic components. However, recovery within the machine tool industry is uneven. Manufacturers focused on mid- to low-end export models face ongoing challenges from weakening demand in China, tariff uncertainty, currency fluctuations, and price competition. In contrast, companies with capabilities in semiconductor and PCB equipment components, high-speed and high-precision machining, or integrated smart production lines demonstrate stronger resilience and growth potential.
Future Outlook: Strategic Focus for 2026
Looking ahead to 2026, the global machine tool market is expected to maintain a pattern of moderate growth with clear structural divergence. Five-axis machining centers, high-speed and high-precision machines, hybrid and additive manufacturing, and smart machines equipped with sensing and AI functions will be key growth segments. For Taiwan, accelerating industrial transformation, strengthening participation in AI, semiconductor, and aerospace supply chains, and expanding into emerging markets such as India, Southeast Asia, Central and Eastern Europe, and Latin America will be critical to enhancing global competitiveness.